Tech Tip: Problems with duplicate fonts and how to fix it
PRODUCT: 4D | VERSION: 13.0 | PLATFORM: Mac & Win
Published On: September 4, 2012
Duplicate fonts can be installed in a system without a users knowledge. For many applications this may not be a problem, but for a 4D developer it can be a hair pulling problem because it will show up on one machine and not on others. It might be in 4D Write, on a screen form, or on a printout. However, the user will sware that it is a 4D problem and not a problem on the machine.
Testing for duplicate fonts on Mac and Windows is different. First, how to find and remove duplicate fonts on a Mac and then on Windows.
On a Mac OS X 6
1) Open the Mac native application Font Book, which is installed in the Application folder.
2) From the Edit menu use "Select Duplicated Fonts"
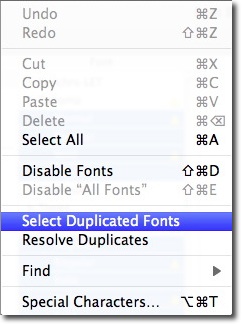
3) The duplicated fonts will be marked with the warning triangle. Hovering over a font brings up a font detail tip.
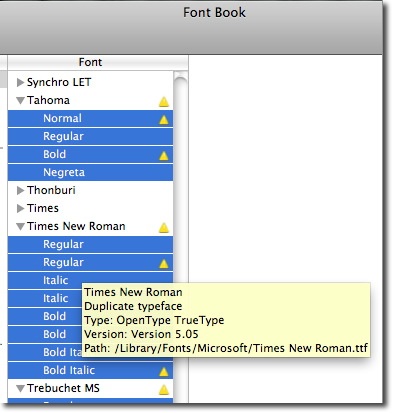
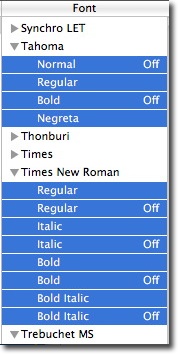
4) Next , from the Edit menu select "Resolve Duplicates"
On a Mac OS X 7 The process is a little simpler.
1) Open the Mac native application Font Book, which is installed in the Application folder.
2) From the Edit menu select "Look for Enabled Duplicates..." (see image below).
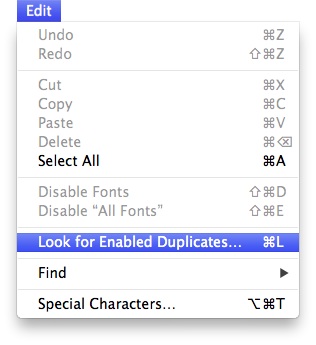
3) Once complete, you can disable the duplicates.
4) To help prevent this in OS X 7 is to enable the preference to "Resolve duplicates by moving files to the Trash."

On Windows
1) Click on "Start" and select "My Computer" (Windows XP) or "Computer" (on Windows Vista and 7).
2) Double-click on "Local Disk (C:)."
3) Double-click on "Windows" and then on "Fonts." A list of all installed fonts will open.
4) Right-click on the duplicate font installation and select "Delete." A duplicate font will have a "[1]" after its name. For example, you will see a file named "Garamond" and "Garamond[1]." In this instance you would right-click on "Garamond[1]" and select "Delete."
Tips & Warnings
Windows automatically adds [1] to a duplicate file located in the same folder. This is Windows way of renaming and keeping both files for the computer owner to review.
Testing for duplicate fonts on Mac and Windows is different. First, how to find and remove duplicate fonts on a Mac and then on Windows.
On a Mac OS X 6
1) Open the Mac native application Font Book, which is installed in the Application folder.
2) From the Edit menu use "Select Duplicated Fonts"

3) The duplicated fonts will be marked with the warning triangle. Hovering over a font brings up a font detail tip.

4) Next , from the Edit menu select "Resolve Duplicates"

On a Mac OS X 7 The process is a little simpler.
1) Open the Mac native application Font Book, which is installed in the Application folder.
2) From the Edit menu select "Look for Enabled Duplicates..." (see image below).

3) Once complete, you can disable the duplicates.
4) To help prevent this in OS X 7 is to enable the preference to "Resolve duplicates by moving files to the Trash."

On Windows
1) Click on "Start" and select "My Computer" (Windows XP) or "Computer" (on Windows Vista and 7).
2) Double-click on "Local Disk (C:)."
3) Double-click on "Windows" and then on "Fonts." A list of all installed fonts will open.
4) Right-click on the duplicate font installation and select "Delete." A duplicate font will have a "[1]" after its name. For example, you will see a file named "Garamond" and "Garamond[1]." In this instance you would right-click on "Garamond[1]" and select "Delete."
Tips & Warnings
Windows automatically adds [1] to a duplicate file located in the same folder. This is Windows way of renaming and keeping both files for the computer owner to review.
